Applications of Mathematics in Computer Science (MACS)
Algorithmic Differentiation
Concepts:
- gradient-based optimization;
- symbolic differentiation;
- numerical differentiation.
Optimization
$$z = −(x^2 + y^2) + 4$$
$$\arg\max\limits_{(x, y)} z = (0, 0)$$
Optimization
- Given: a function $f : A \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$
- Find: $x_0 \in A$ such that $f(x_0) \le f(x)$ for all $x \in A$ — "minimization", or $\ge$ — maximization.
Examples
- shortest path in graph
- job with highest salary
- best vaccination strategy for COVID
Stochastic optimization
We can try many values randomly:

Gradient-based optimization
Gradient: $\nabla f = \begin{pmatrix} \frac {\partial f} {\partial x_1}\\ \frac {\partial f} {\partial x_2} \\ ... \end{pmatrix} $ — direction of fastest ascent.
With $\nabla f(x, y, ...)$ we can optimize much faster.
Gradient descent
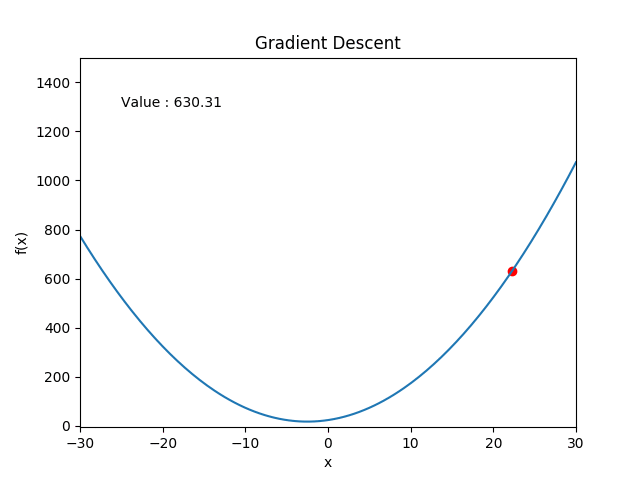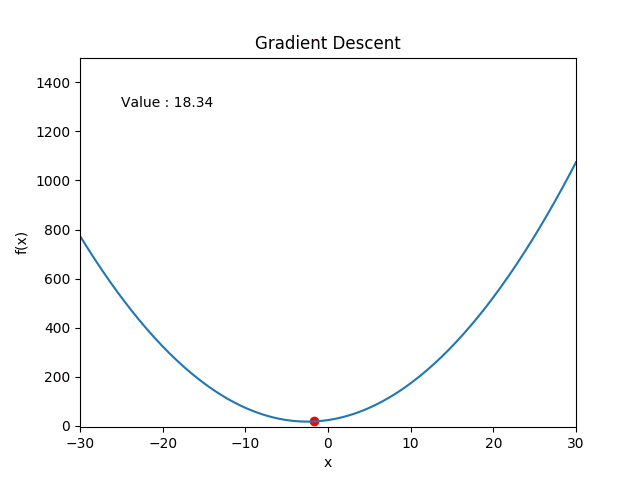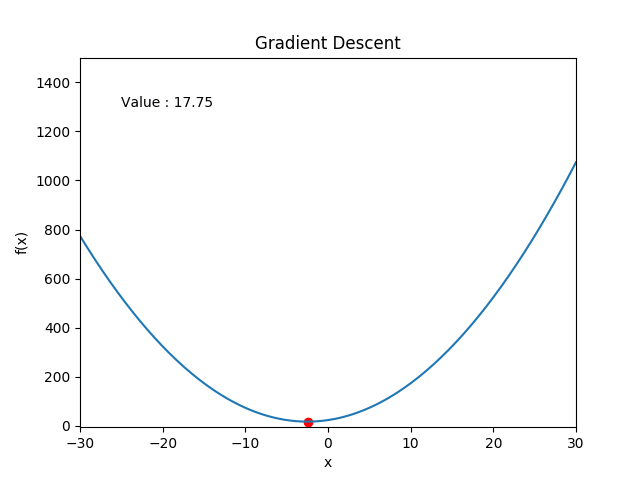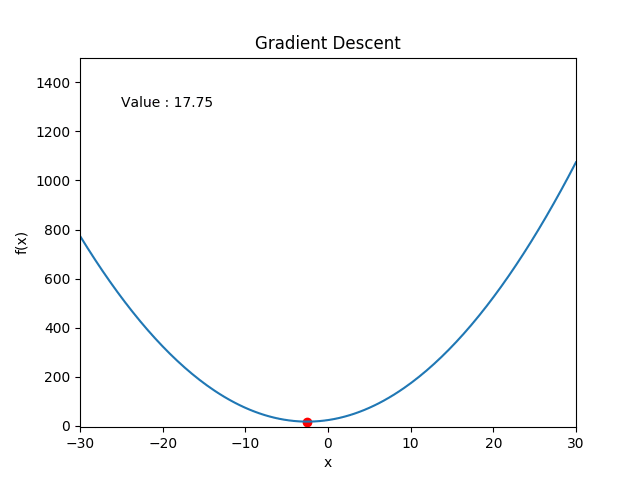
-
Repeat:
- $x \gets x - \delta\nabla f(x)$
- $\delta \gets \gamma\delta$
- where
- $\delta$ is small
- $\gamma = 1 - \varepsilon$
Newton's method

-
Repeat:
- $x \gets x - \frac {f''(x)} {f'(x)}$
- converges faster than GD
How to obtain derivatives?
$$\nabla f(x)$$ $$f'(x)$$ $$f''(x)$$ $$...$$
Differentiation
- Slope of the function's tangent
- $f'(x) = \lim\limits_{h \to 0} \frac {f(x+h) - f(x)} {h}$
- also $\frac {df} {dx}$ (Leibniz's notation)
- Partial derivatives: $\frac {\partial f(x_1, x_2, ..., x_n)} {\partial x_i}$
Differentiation rules
- Constant rule: if $f(x)=C$ then $f'(x)=0$
- Sum rule: $(f(x) + g(x))' = f'(x) + g'(x)$
- Product rule: $(f(x)g(x))' = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)$
- Quotient rule: $\left(\frac 1 {f(x)}\right)'=-\frac {f(x)'} {f(x)^2}$
- Chain rule: $f(g(x))' = f'(g(x))g'(x)$
Differentiation examples
$$1' = 0$$ $$x' = 1$$ $$\left(x^2\right)'= xx' + x'x = 2x$$ $$sin(x)' = cos(x)$$ $$tan(x)' = \left( \frac {sin(x)} {cos(x)}\right)' = \frac {sin^2(x) + cos^2(x)} {cos^2(x)} = \frac 1 {cos^2(x)}$$ $$...$$How do computers differentiate?
- Numerical differentiation
- Symbolic differentiation
- Algorithmic differentiation
Numerical differentiation
- Choose $h$
- Compute $f(x)$
- Compute $f(x+h)$
- Return $\frac {f(x+h) - f(x)} h$
Problems
- $h$ too large — truncation error (שגיאת קיטום)
- $h$ too small — roundoff error (שגיאת עיגול)
Symbolic differentiation
- Represent function symbolically.
- Apply differential rules.
Problems
- Loops, conditionals, recursion.
- Code swell:
\begin{equation} \begin{aligned} \left( \frac {\log(x) + \exp(x)} {\log(x)\exp(x)}\right)' = & -\frac {\exp(-x)(\log(x)+\exp(x))} {\log(x)} \\ & -\frac {\exp(-x)(\log(x)+\exp(x))} {x\log^2(x)} \\ & + \frac {\exp(-x)\left(\exp(x) + \frac 1 x\right)} {\log(x)} \end{aligned} \end{equation}
Algorithmic differentiation
- NOT symbolic differentiation
- NOT numerical differentiation
- differentiates ANY code
- computation costs of $f'(x)$ and $f(x)$ are similar
Algorithmic differentiation
def f(a, b):
c = a*b
d = sin(c)
return d
def f(a, da, b, db):
c, dc = a*b, da*b + a*db
d, dd = sin(c), dc * cos(c)
return d, dd
Program trace
f.py
def f(a, b):
c = a*b
if c > 0:
d = log(c)
else:
d = sin(c)
return d
f(2, 3)
a=2, b=3
c=a*b=6
d=log(c)=1.791
return d=1.791
f(2, 3), df(2, 3)/da
a=2, b=3, da=1, db=0
c=a*b=6, dc=da*b + a*db=3
d=log(c)=1.791, dd=dc*(1/c)=0.5
return d=1.791, dd=0.5