Applications of Mathematics in Computer Science (MACS)
Google PageRank
Concepts:
- graph adjacency matrix;
- graph centrality;
- eigenvalues;
- eigenvectors.
CS problem: Ranking nodes
- We are given a directed graph $G=(V, E)$ (WWW pages, scientific papers, people relations)
- How do we rank nodes in the graph
Example: Internet search (page order on search page)
Graph adjacency matrix
- A directed graph of four vertices: $v_1, v_2, v_3, v_4$.
- Five edges: $e_{1,2}, e_{2,1}, e_{1, 3}, e_{1, 4}, e_{2, 4}$.
Adjacency matrix: $$A=\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}$$ $a_{ij}\ne0 \Leftrightarrow$ there is an edge from $v_i$ to $v_j$.
Edge weights
Edges may have weights (e.g. edge length):
$$A=\begin{pmatrix}
0 & 0.5 & 4 & 1\\
0.25 & 0 & 0 & 4 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0
\end{pmatrix}$$
Undirected graph
$A$ of undirected graph is symmetric:
$$A=\begin{pmatrix}
0 & 0.5 & 4 & 1\\
0.5 & 0 & 0 & 4 \\
4 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
1 & 4 & 0 & 0
\end{pmatrix}$$
$a_{ij}=a_{ji}\,\forall i, j$
Vectors and matrices
- vectors are 1-dimensional: $\pmb{v}=\begin{pmatrix}v_1 \\ v_2 \end{pmatrix}$
- matrices are 2-dimensional: $\pmb{A}=\begin{pmatrix}a_{11} & a_{12} \\ a_{21} & a_{22}\end{pmatrix}$
A scalar is a vector (or a matrix) with 1 element.
Matrix multiplication
$$C = AB\,\Rightarrow\,c_{ij} = \sum_k a_{ik} b_{kj}$$$\begin{pmatrix}2\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}3\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}6\end{pmatrix}$
$\begin{pmatrix}2 & 1 \\-1 & 2\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}1 \\ -1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}1\\-3\end{pmatrix}$
$\begin{pmatrix}2 & 1 \\-1 & 2\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}1&2 \\ -1&1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}1&5\\-3&0\end{pmatrix}$
Matrix inverse
$$AA^{-1} = I,\, i_{ii}=1, i_{ij}=0 \mbox{ if } i \ne j$$$I_{2\times2}=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\0 & 1\end{pmatrix}$
$\begin{pmatrix}2 & 1 \\-1 & 2\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0.4&-0.2 \\ 0.2&0.4\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}1&0\\0&1\end{pmatrix}$
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- Vectors are scaled and rotated by matrices. $$\begin{pmatrix}1 & -1 \\-1 & 1\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}2\\1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}1\\-1\end{pmatrix}$$
-
Some vectors are only scaled.
$$\begin{pmatrix}1 & -1 \\-1 & 1\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}-1\\1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}-2\\2\end{pmatrix}$$
They are eigenvectors.
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
If $Av=\lambda v$ then
- $v$ — eigenvector (וקטור עצמי)
- $\lambda$ — eigenvalue (ערך עצמי)
$$A=\begin{pmatrix}1 & -1 \\-1 & 1\end{pmatrix}$$
- Eigenvectors: $v_1=\begin{pmatrix}1\\1\end{pmatrix}, \, v_2=\begin{pmatrix}-1\\1\end{pmatrix}$
- Eigenvalues: $\lambda_1=0,\, \lambda_2=2$
Google PageRank
- A search engine finds some pages.
- Pages must be sorted.
- How to assign page importance? PageRank ($R$)
- Measures centrality
Simplified PageRank
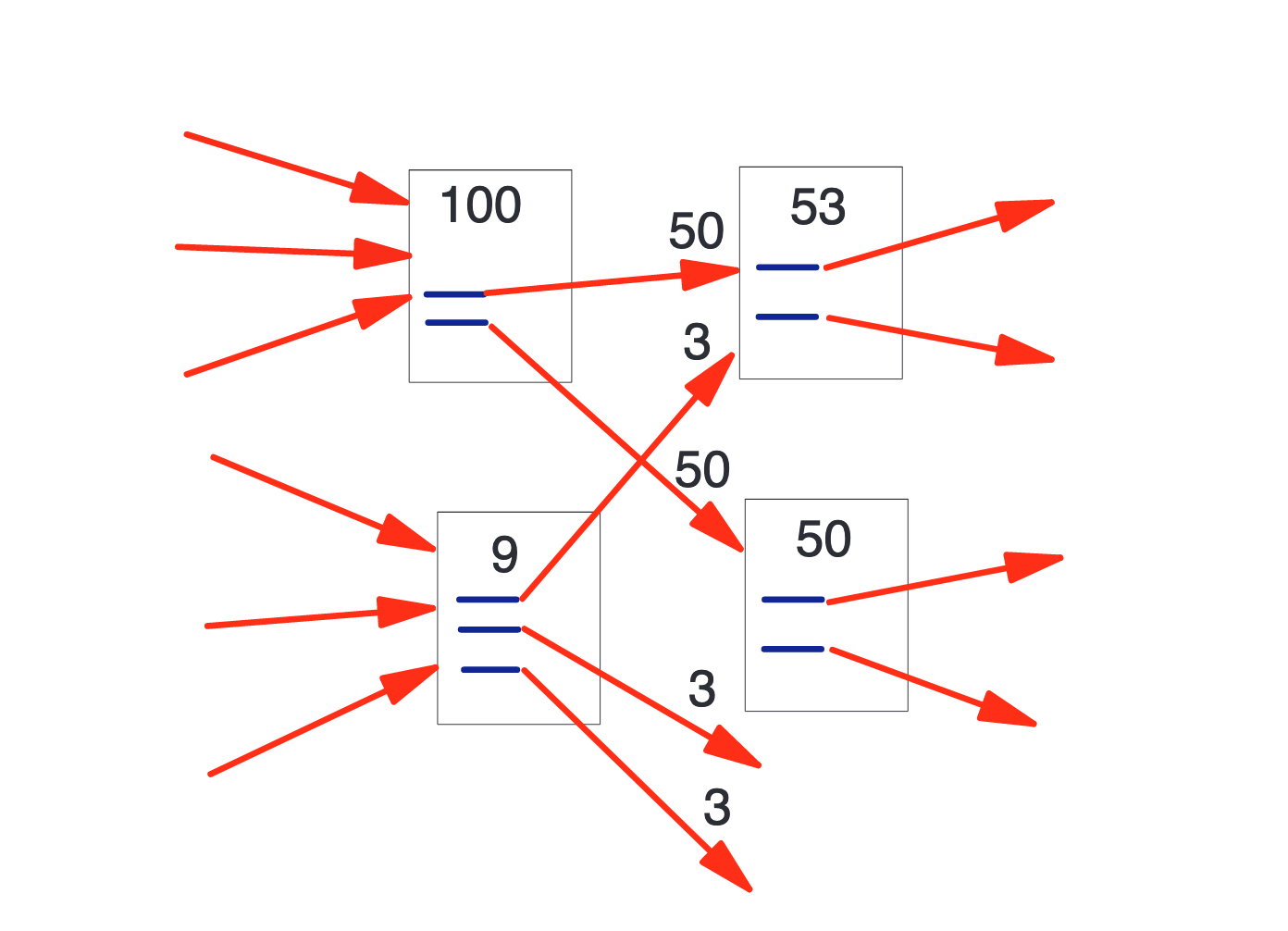 $$R(u) = \sum_{\forall (v, u)} \frac {R(v)} {Nv}$$
$$R(u) = \sum_{\forall (v, u)} \frac {R(v)} {Nv}$$
Simplified PageRank
$$R = AR$$$$a_{ij}=$$
- $\frac 1 {N_i}$ if edge $(j, i)$ in the graph,
- otherwise 0.
$R$ is an eigenvector with eigenvalue $1$!
PageRank
Users stay with probability $d$ --- the damping factor
. \begin{align} R = & \frac {1-d} N\mathbf{1} + dAR,\, d \le 1 \,(\approx 0.85) \\ = & \left( \frac {1-d} N \mathbf{E} + dA \right)R \end{align}$$a_{ij}=$$
- $\frac 1 {N_i}$ if edge $(j, i)$ in the graph,
- otherwise 0.
$R$ is an eigenvector with eigenvalue $d < \pmb{\lambda} < 1$!
PageRank computation
Iterative (power iteration):
- Set: $R_i = \frac 1 N\, \forall i$
- At each step: $R' = \frac {1-d} N\mathbf{1} + dAR$
- Stop when: $|R'-R| < \varepsilon$
- $R \gets R'$